|
Ethernet Bridge RS-232/RS-422/RS-485 |
ESB-1 or ESB-2 RS-232/RS422/RS485
Asynchronous Ethernet Bridge
Ethernet Bridge ESB-1 or ESB-2 RS-232, RS422, RS485
Asynchronous Ethernet Bridge
for SCADA data
12, 24, 48, 125 VDC
115VAC power and 220/230 VAC also available
ESB-1 or ESB-2 Etherseries Asynchronous Ethernet Bridge

|
- No configuration, easy setup mode
- Learning, Ethernet bridge
- Protocol independent
- No routing configuration required..... ever
- 10/100BaseT Ethernet interface
- RS-232/422/485 interface at 230.4 Kbps
- Available with optional 2nd independent WAN port
- Ideal companion to 900 mHz and 2.4 gHz spread
spectrum
wireless modems
- Advanced Management allows SNMP, Web-browser,
telnet, or terminal management
|
FEATURES
- No configuration, easy setup mode
- Learning, Ethernet bridge
- Protocol independent
- No routing configuration required.… ever
- 10/100BaseT Ethernet interface
- Available with optional 2nd independent WAN port
- RS-232/422/485 interface at 230.4 Kbps
- Ideal companion to 900 mHz and 2.4 gHz spread spectrum wireless modems
- Advanced Management allows SNMP, Web-browser, telnet, or terminal
management
DESCRIPTION
The ESB-1 EtherSeries Bridge is an easy to use Ethernet bridge. The link between
the EtherSeries Bridges is asynchronous RS-232, RS-422, or RS-485 (4 wire)
running at speeds between 300 bps and 230.4 Kbps.
The EtherSeries Bridge is available with a second WAN port, which is ideal
for higher density host sites or daisy chaining bridges, commonly used for SCADA
applications.
The EtherSeries Bridge is 100% protocol independent. It will bridge TCP/IP,
AppleTalk, DecNet, Netbui, or any protocol that can be transported over
Ethernet. This makes the EtherSeries Bridge easy to set up. No configuration is
necessary.
The EtherSeries Bridge transfers data over the bridge only if it is destined
for an Ethernet address (MAC layer address) on the other side of the bridge.
Traffic is filtered, much the same way an Ethernet switch filters Ethernet
traffic, to maximize available bandwidth. Unless advanced management is
required, no IP address is involved and there is no set-up other than matching
serial port speeds. Advanced management allows SNMP, web-browser, and telnet
based management of the bridge.
The EtherSeries Bridge learns the addresses quickly. This allows, for
example, a technician to be working at one end of the bridge with a laptop
computer, then move the laptop to the other side, with no need to reset the
bridge. The bridge learns within a few packet times that the computer and its
Ethernet address moved to the other side of the bridge.
The EtherSeries bridge is much easier to use than a router. There is no IP
address that must be set up in the bridge. There is no subnet mask to setup.
There is no destination IP address to setup. You just plug it in and use the
network. Popular in the early 90's, bridging technology was often abandoned as
communication equipment hardware grew to offer routing capability. However,
using a router for small networks adds tremendous complexity, overhead, and
requires knowledge of protocols and IP subnetting. In addition, there are many
non-routable protocols in use. The availability of an inexpensive Ethernet WAN
bridge now brings back those economies and simplicity for LAN connections that
typically use fewer than several hundred computers.
SPECIFICATIONS
General
- Management Methods
- Any Web Browser
- Telnet Menu Interface
- Direct Connection Menu Interface
- SNMP (get and trap) functionality included
- RS-232 serial port, DTE interface
- DE-9 RS-232 male serial DTE (terminal interface) port
- Serial speeds from 300 bps to 230,000 bps
- RJ45 10 BaseT and 100BaseT Ethernet, autoselected
- Management via telnet command line interface, the serial port, or any web
browser
Indicators
Link and Activity LEDs
Controls
One Press button switch used to establish operating mode.
Interface: RS-232, V.24, speeds up to 230,000 bps asynchronous
Connector: DE-9P RS-232 (commonly known as a DB-9 PC connector)
LAN Connection
Interface: 10BaseT or 100BaseT
- 4" 1/4" x 5 1/2 " x 1 1/2 "
- 1 LB
- -40 to +70 C, <95% non-condensing RH
- 9 to 12 volt DC external 110 VAC power supply
12, 24, 48, 125 VDC and 240 VAC also available
- Less than 300 mA at 9 volts
- 15 watts max power consumption
|

Front view of DCB EtherSeries Bridge
RS-232 Connector
|

Rear view of DCB EtherSeries Bridge
LAN Connectors
|
Application
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
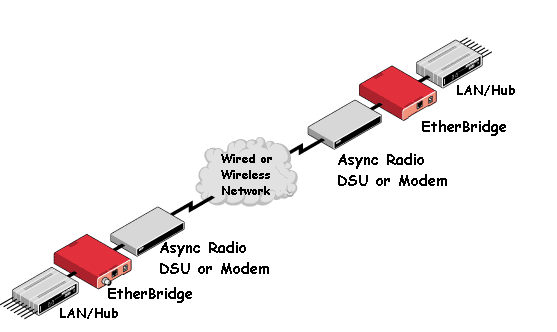
- Connecting a remote computer or LAN to a host LAN via slow-speed
communications paths
- Connecting remote SCADA equipment having a Ethernet interface to a
remotely located host
- Connecting host computers to remote equipment via asynchronous connections
| ESB-1 |
1 Serial Port EtherSeries Bridge |
| ESB-2 |
2 Serial Port EtherSeries Bridge |
Related pages
Stat Mux, Statistical
Multiplexer, FRAD, Routers,
Wireless, Remote Access,
RS-232, modems,
SCADA, and LAN interconnection
equipment
see other pages
ARC ELECTRONICS
301-924-7400 EXT 25
jump to ... Home Page
arc@arcelect.com



