|
NEBS |
NEBS
Network
Equipment Building
System
What
is NEBS and why is it important? Long a requirement for equipment used in
the Central Office in the North American Public Switched Network, the rigorous Network
Equipment Building
System (NEBS) criteria have become a
universal measure of network product excellence. The NEBS compliance of GDC's
products is a key advantage for access providers including Local Exchange
Carriers (LECs), Competitive Access Providers (CAPs), Competitive Local Exchange
Carriers (CLECs), Internet Service Providers (ISPs), and Access Service
Providers (ASPs). Products that are NEBS certified are also expected to be top
performers in enterprise net- work environments as well.
Q: How and why NEBS was developed?
All
electronic equipment has the potential to interfere with other electronic
equipment. Interference can be caused by electromagnetic radiation, the
grounding system, the electrical power connection, excessive heat or blocking
the natural air flow, and connecting wires or cables. The FCC (Federal
Communications Commission) regulates a portion of this problem through Part 15
of their rules and regulations, which specifies a maximum allowable amount of
electromagnetic radiation from an electronic device in a commercial or
residential environment at specific frequencies.
Another
standard that addresses the issue of collocated electronic equipment is NEBS.
Telephone companies typically place a large amount of network equipment, often
from different manufacturers, into relatively tight association, especially in
their central office buildings. To address this, they gathered the best thinking
from the FCC and various national and international trade and standards groups
to create a set of specifications for network facilities located equipment.
Originally developed by Bell Telephone Laboratories in the 1970s and expanded by
Bellcore, these requirements are known as Network Equipment Building System
(NEBS) Requirements.
The
most referenced documents in the United States telecommunications industry on
the subject, the "NEBS Criteria" as they are usually called, are
designed to help assure that the equipment purchase is easy to install, operates
reliably, and efficiently occupies building space. The expectation is that
physical configurations and compatibility of equipment with a set of
environmental conditions will help to reduce product installation and
maintenance costs.
Bellcore introduced the NEBS requirements in 1985 as a public document, with manufacturers of central office equipment as the target audience. This introduction extended the principles from the pre-divestiture Bell Labs focus of telephone companies to the growing industry of equipment manufacturers supplying a broad range of telecommunications equipment.
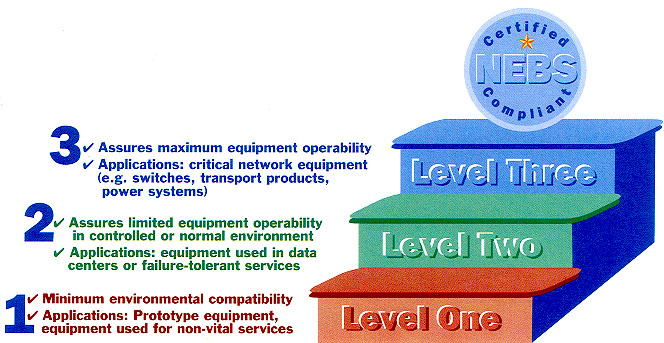
Regional
operating companies and inter- exchange carriers require NEBS compliance. NEBS
is a baseline for vendor selection and deployment by a new generation of service
providers, such as competitive local exchange carriers, Internet service
providers, independent telephone companies and others.
Q:
Briefly, what is specified in the NEBS requirement?
Even
more stringent than the FCC Part 15 requirements, NEBS covers a large range of
requirements including criteria for personnel safety, protection of property,
and operational continuity. The Bellcore documents cover both physical
requirements including: Space Planning, Temperature, Humidity, Fire, Earthquake,
Vibration, Transportation, Acoustical, Air Quality and Illumination; and
electrical criteria including: Electrostatic Discharge (ESD), Electromagnetic
Interference (EMI), Lightning and AC Power Fault, Steady State Power Induction,
Corrosion,, DC Potential Difference, Electrical Safety and Bonding and
Grounding.
Q:
What are the objectives of these criteria? NEBS criteria are designed to
accomplish the following:
•
Ensure equipment compatibility with the telephone industry's electrical
environment
• Simplify equipment planning and installation
•
Protect telecommunications equipment from service outages caused by
incompatible equipment
•
Prevent interference to licensed radio transmitters and other close
proximity telecommunications equipment
•
Minimize the risk of fires to telecommunications equipment
•
Ensure equipment operation under the range of temperature, humidity,
vibration, and airborne contamination present in telecommunications locations
•
Ensure equipment and service survivability in the event of earthquake
•
Protect personnel from injury
Q:
Does NEBS have any importance beyond the telephone company world?
NEBS
is a major test of quality that is extremely valuable for any organization
supplying or purchasing network equipment. A product that is NEBS certified has
passed a suite of tests ensuring that the product will: operate reliably and be
serviceable; not negatively affect other service providing equipment; operate
properly in adverse environmental conditions; and not cause harm to the
environment or personnel. Non-NEBS certified equipment may cause operating
problems with other equipment, either instantaneously or over a long period of
time. This equipment may also not perform properly or have a high failure rate
and may result in very difficult to isolate network problems or failures.
ARC
ELECTRONICS
301-924-7400 EXT 25
jump to ... Home
Page
arc@arcelect.com